Star Dust Babies
We are STAR DUST !


The time is now 5:24 pm
You last visited
May 6, 2024, 4:27 pm
All times shown are
Eastern Time (GMT-5:00)

We are STAR DUST !
When I first saw this, I thought this was real, but it is an incredible animation of the real person, which you will see at the very end, but even then you can't tell....lol
I don't know if this is real but having driven rigs myself, I can't see any reason for this to happen other than the driver of the rig doing this on purpose.
WARNING ! ! !
Maybe graphic to some.
My first question was a simple one. If the owners of the tape have the full version, why not show it? Why show certain still images? Someone did ask that question in the comment section, but the answer was totally unsatisfactory, atleast to me.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5gTH_9qt7yY
Spooky nonetheless.....
The Pope has it but he does not use it.
Your father has it but your mother uses it.
Nuns do not need it.
Arnold Schwarzenegger has a big one,
Michael J. Fox’s is quite small.
What is it?
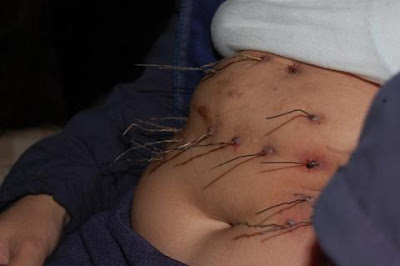
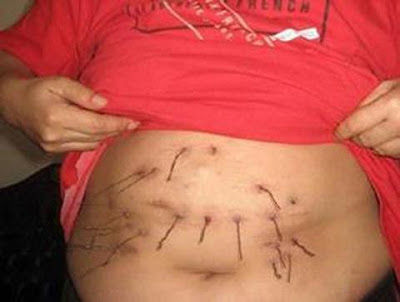

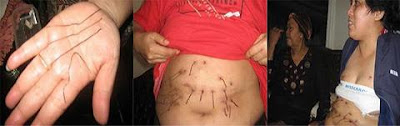
all.
Last week's excitement over a supposed Bigfoot body, which culminated Friday in a circus-like press conference in Palo Alto, Calif., collapsed like a wet soufflé Sunday as an independent investigator determined it was all fake.
SearchingforBigfoot.com owner Tom Biscardi had paid an "undisclosed sum" — Internet rumors put it at $50,000 — to Georgia residents Matthew Whitton and Rick Dyer for their frozen "corpse" and the privilege of trotting them, but not the body, out in front of TV cameras.
At the same time, Biscardi sent self-described "Sasquatch detective" Steve Kulls to a secret location — apparently Muncie, Ind. — to check out the specimen.
Kulls, it's safe to say, was severely disappointed.
The upshot? Bigfoot, once found, is now again missing. So are Whitton, Dyer and Biscardi's
In a long statement on SearchingforBigfoot.com, Kulls reveals what he found early Sunday morning Eastern time as the body thawed out.
"I extracted some [hair] from the alleged corpse and examined it and had some concerns," Kulls writes. "We burned said sample and said hair sample melted into a ball uncharacteristic of hair."
Kulls called Biscardi in California, who told him to heat the body to speed up thawing.
"Within one hour we were able to see the partially exposed head," Kulls continues. "I was able to feel that it seemed mostly firm, but unusually hollow in one small section. This was yet another ominous sign."
Then came the clincher.
"Within the next hour of thaw, a break appeared up near the feet area. ... I observed the foot which looked unnatural, reached in and confirmed it was a rubber foot."
That jibes with what Jerry Parrino, owner of Internet Halloween-costume retailer TheHorrorDome.com, told FOXNews.com last week.
"It definitely looks like our [Sasquatch] costume," Parrino said after viewing photos of the body.
The Biscardi team immediately went into crisis mode. Biscardi called Whitton and Dyer at their California hotel.
They admitted it was a hoax and agreed to sign a promissory note at a meeting set for 8 a.m. Pacific time at the hotel.
But when Biscardi got there, he "found that they had left."
"At this time action is being instigated against the perpetrators of this fraud," Kulls writes on Biscardi's Web site. "On behalf of myself I can say with certainty Matthew Whitton and Ricky Dyer [are] not the best Bigfoot trackers in the world!"
Loren Coleman, who runs the influential Cryptomundo.com Web site devoted to mysterious animals, isn't buying Biscardi's pleas of ignorance.
"He's a huckster, a circus ringmaster," Coleman told FoxNews.com. "It's all about money with him. It probably didn't matter to him whether it was real or not."
So why would Dyer, described as a former security guard, and Whitton, a police officer with the Clayton County, Ga., department, make it all up?
"They probably started out small, as a way to promote their Bigfoot tracking business, and got in way over their heads," Coleman figured. "These are not very intelligent individuals."
The involvement of Biscardi, who Coleman says was introduced to the pair by Kulls, brought them attention they didn't need.
"In a way, both sides may have been trying to out-con each other," said Coleman.
The Bigfoot Field Research Organization, another Bigfoot group that refused to take seriously what Coleman dubbed the "Georgia gorilla," wants everyone connected with the "body" — Biscardi, Dyer, Kulls and Whitton — arrested.
"Warrants need to be issued immediately before Biscardi leaves the country," the organization's Web site states.
As for Whitton, he doesn't seem to have a job to come back to in Georgia.
Asked for comment on Officer Whitton, Clayton County, Ga., Chief of Police Jeffrey Turner, corrected FoxNews.com. "You mean ex-officer Whitton."
"As soon as we saw it was a hoax," Chief Turner explained, "I filed the paperwork to terminate his employment."
Turner said he hasn't heard from Whitton, and that he was mystified at the former officer's involvement in such a blatant scam.
"He was a real go-getter," Turner said, citing Whitton's wounding in the line of duty earlier this summer while apprehending a suspect who had allegedly shot a woman in the head. "For someone to do a complete three-sixty like that, I can't explain it."
The woman who answered the phone at Biscardi's Searching for Bigfoot office in Menlo Park, Calif., said he was out ill but would return calls when he could.
Brings back good memories.....lol
Reminiscing lane....

With every telephone call, swipe of a card and click of a mouse, information is being recorded, compiled
and stored about Britain's citizens.
An investigation by The Sunday Telegraph has now uncovered just how much personal data is being collected about individuals by the Government, law enforcement agencies and private companies each day.
In one week, the average person living in Britain has 3,254 pieces of personal information stored about him or her, most of which is kept in databases for years and in some cases indefinitely.
The data include details about shopping habits, mobile phone use, emails, locations during the day, journeys and internet searches.
In many cases this information is kept by companies such as banks and shops, but in certain circumstances they can be asked to hand it over to a range of legal authorities.
Britain's information watchdog, the Information Commissioner's Office, has called for tighter regulation of the amount of data held about citizens and urged the public to restrict the information they allow organisations to hold on them.
This newspaper's findings come days after the Government published plans to grant local authorities and other public bodies access to the email and internet records of millions. Phone companies already retain data about their customers and give it to 650 public bodies on request.
The loss of data by Government departments, including an incident where HM Revenue and Customs mislaid computer disks containing the personal details of 25 million people, has heightened concerns about the amount of information being stored.
David Smith, deputy information commissioner, said: "As more and more information is collected and kept on all of us, we are very concerned that appropriate safeguards go along with that.
"People should know what is happening with their information and have a choice.
"Our concern is that what is kept with the justification of preventing and detecting terrorism, can then be used for minor purposes such as pursuing people for parking fines."
Earlier this year the Commons home affairs select committee recommended new controls and regulations on the accumulation of information by the state.
Every day the average person makes three mobile phone calls and sends at least two text messages.
Each time the network provider logs information about who was called as well as the caller's location and direction of travel, worked out by triangulation from phone masts.
Customers can also have their locations tracked even when they are not using their phones, as the devices send out unique identifying signals at regular intervals.
All of this information can be accessed by police and other public authorities investigating crimes.
Internet service providers (ISPs) compile information about their customers when they go online, including name, address, the unique identification number for the connection, known as an IP address, any browser used and location.
They also keep details of emails, such as whom they were sent to, together with the date and time they were sent. An average of 50 websites are visited and 32 emails sent per person in Britain every day.
Privacy campaigners have expressed concern that the country's three biggest ISPs – BT, Virgin Media and TalkTalk – now provide this data to a digital advertising company called Phorm so that it can analyse web surfing habits.
ISPs are already voluntarily providing information they hold about their customers if requested by law enforcement agencies and public authorities. A consultation published last week by the Government would make it a legal requirement for ISPs to provide a customer's personal information when requested. A total of 520,000 requests were made by public officials for telephone and internet details last year, an increase from around 350,000 the previous year.
Internet search engines also compile data about their users, including the IP address and what was searched for. Google receives around 68 searches from the average person each day and stores this data for 18 months.
Dr Ian Brown, a research fellow on privacy at Oxford University, said: "Companies such as Google and internet service providers are building up huge databases of data about internet users.
"These companies may be compelled, through a legal action, to hand over this information to third parties or the Government, or the companies may lose the data and it can then be misused."
Store "loyalty" cards also retain large amounts of information about individuals who have signed up to use them. They link a person's personal details to the outlets used, the transaction times and how much is spent.
In the case of Nectar cards, which are used by more than 10 million people in Britain once a week, information from dozens of shops is compiled, giving a detailed picture of a cardholder's shopping habits.
A spokesman for Loyalty Management UK, which runs the Nectar programme, insisted that information about the items bought was not compiled, but some partners in the scheme, such as Sainsbury's, use their till records to compile that information.
She admitted that the personal information that is compiled under the Nectar scheme is kept indefinitely until individuals close their account and ask for their information to be destroyed. In criminal inquiries, police can request the details held by Nectar.
Banks can also be required to hand over personal account information to the authorities if requested as part of an investigation.
They also provide personal data to credit reference agencies, debt collectors and fraud prevention organisations.
Debit and credit card transactions can give information about where and on what people are spending their money.
The biggest source of surveillance in Britain is through the network of CCTV (closed-circuit television) cameras. On average, an individual will appear on 300 CCTV cameras during a day and those tapes are kept by many organisations for indefinite lengths of time.
On the London Underground network, Transport for London (TfL) keeps footage for a minimum of 14 days. TfL operates more than 8,500 CCTV cameras in its underground stations, 1,550 cameras on tube trains and up to 60,000 cameras on buses.
Network Rail refused to say how many CCTV cameras it operates or for how long the footage is kept.
Britain now has more CCTV cameras in public spaces than any other country in the world. A study in 2002 estimated that there were around 4.2 million cameras, but that number is likely to now be far higher.
The latest development in CCTV is the increased use of automatic number plate recognition systems, which read number-plates and search databases for signs that a vehicle has been used in crime.
A national automatic number plate recognition system is maintained by the Association of Chief Police Officers along motorways and main roads. Every number plate picked up by the system is stored in a database with date, time and location for two years.
Travel passes such as the Oyster Card used in London and the Key card, in Oxford, can also reveal remarkable amounts of information about an individual. When they are registered to a person's name, they record journey history, dates, times and fares.
A spokesman for TfL, which runs the Oyster Card system, insisted that access to this information was restricted to its customer services agents.
Police, however, can also obtain this information and have used Oyster Card journey records as evidence in criminal cases.
Employers are increasingly using radio-tagged security passes for employees, providing them with information about when staff enter and leave the office.